Differences in the selectivity of reversed-phase columns
Columns for reversed-phase chromatography are developed and sold by various column manufacturers. The separation behavior of the target compound may vary greatly depending on the column brand or series, even if the functional group is the same. These differences in separation behavior are caused by the difference in carbon content due to the method of chemical modification of functional groups, the difference in pore size of the substrate, the end capping treatment for silica gel and organosilica substrates to reduce residual silanol groups in the substrate, and the difference in the material of the column body (see Table 1).
Table 1
| Examples | Remarks |
|---|---|
| Differences in Carbon Content | Generally, the larger the carbon content, the stronger the retention capacity for compounds in reversed phase mode. |
| Differences in Pore Size | Depending on the relationship between pore size and compound size, the diffusion of the compound within the packing material changes, and so the retention capacity for the compound changes. |
| End Capping | · End capping reduces the residual silanol in the base material in columns in which silica base materials and organosilica base materials are used · The chemical interactions with the compounds change |
| Differences in Column Tube Materials | Depending on differences in the materials in the column’s wetted parts, interactions with the compounds change, which can have a particular impact on the degree of compound adsorption. |
As an example, we used 26 different types of C18 columns from different manufacturers and brands, and summarized the relationship between carbon content and retention in Fig. 1 below. Fig. 1 shows that there is a positive correlation between carbon content and retention. (Calculations of particle parameters such as carbon content and surface area vary from manufacturer to manufacturer.)
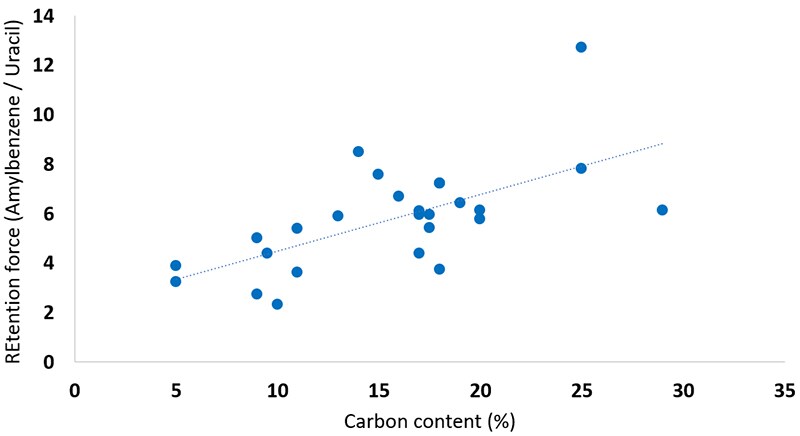
Fig.1






