Neurorehabilitation Application Research
In recent years, progress has been made in researching the use of fNIRS in neurorehabilitation applications, such as during or after a stroke. PET and fMRI systems require the patient to be at rest, but fNIRS systems can measure brain function even while the patient is performing tasks that involve body movement. Therefore, it can be used to obtain information about cerebral activity associated with walking or other movement.
The above shows the brain activity measured while walking on a treadmill. It shows an increase in Oxy-Hb associated with walking, inner side of the primary sensorimotor cortex, near the center. fNIRS is able to measure brain activity during dynamic movements assigned as tasks, such as walking or arm swinging, which cannot be measured using fMRI and PET. It can also be used to assess brain activity at the bedside. fNIRS is being used in research to evaluate brain activity during hemiplegic gait by stroke patients, to improve asymmetry in the activity of the sensorimotor cortex, increase activity in the premotor cortex, improve walking, etc.
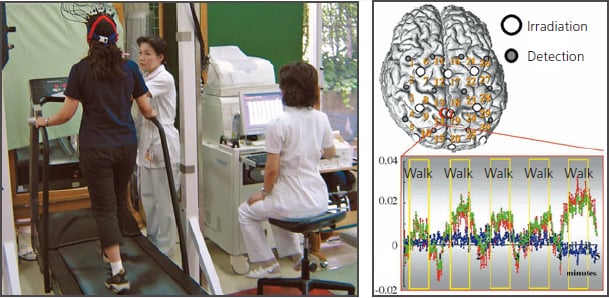
fNIRS Measurement of Brain Activation while Walking on a Treadmill
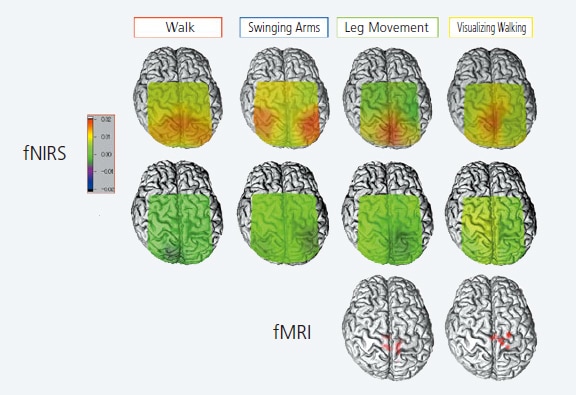
Brain Activity for Healthy Person during walking and Related Tasks
(Data provided by: Mr. Ichiro Miyai, Morinomiya Hospital, Omichi-kai Medical Corporation)
Reference: Miyai, I., (2004). "Application of fNIRS in Neurorehabilitation." MEDICAL NOW, No. 52: 33-36.
Note: The data shown was acquired using a FOIRE/OMM series model.
Related Products

LABNIRS
functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy System for Research
The laboratory model is ideal for a wide variety of basic research fields.
With a broad range of possible measurement regions, it can be readily customized for specific experimental conditions.

LIGHTNIRS
Portable functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy System for Research
The portable model is ideal for field research.
It expands the possibilities for measuring brain function in a diverse range of applications and research fields.


