Vial and Crimper - Features
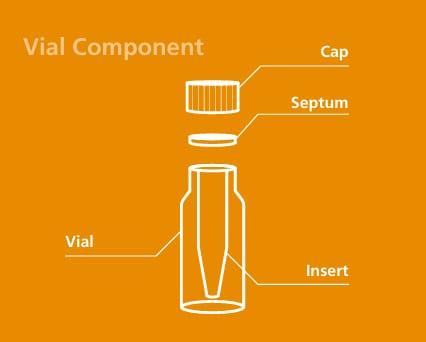
Vial Components
Mainly composed of a vial, cap, and septum, and sometimes used with a vial insert placed inside the vial.
To obtain the best analysis results, the most appropriate vial, cap, and septum need to be selected. Select the most appropriate items using this guide as a reference.
Vial
Vial Glass
Vial glass is manufactured from chemically very low active glass. Type I borosilicate glass (33 or 51 Expansion), which is the highest grade in the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) and European Pharmacopoeia (EP) standards, has been adopted.
Deactivated Glass
Suitable for chemical compounds that are easily adsorbed onto glass. The polarity of the glass surface is reduced by silanization to make the glass surface hydrophobic. It is also suitable for storing samples.
Vial Form
Vial neck

There are three types of vials: screw, crimp, and snap, according to the cap attachment method.
Since highly volatile solvents are often used with GC and GC-MS, airtight screw neck or crimp neck vials are recommended.
| Type | Sealing property | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Screw | High | Screw type caps can be attached and detached easily. Highly versatile. |
| Crimp | Very High | Requires a dedicated crimping tool (crimper/decapper). |
| Snap | Medium | No tools are required, but the airtightness is rather inferior. |
Vial bottom

Vial bottom
Flat-bottom vials are used in most cases, but vials for headspace have rounded bottoms for compatibility with headspace samplers.
Rounded bottom vials should be used with the HS-20 series and HS-10 since flat-bottom vials may cause a malfunction.
Insert

Vials for Microscale Samples
When the sample volume is less than 1 mL, using vial inserts or integrated vials in which an insert is adhered inside the vial ensures liquid levels that are high enough to be aspirated by an autosampler.
Septum
Obtaining accurate analysis results requires selecting the appropriate septum. A septum is influenced by penetration of the autosampler needle, interaction between the solvent used in analysis, the heat by headspace analysis, etc., so features such as its seal-ability, deactivation to the sample and heat resistance need to be considered.
| Material | Heat resistance temperature | Appearance | Description | for headspace |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE |  |
The chemical resistance is stable, and the septum is inexpensive. Since it cannot be tightly sealed once a hole is made, it is not suitable for multiple injections and long-term sample storage. | ||
| Silicone / PTFE | 200℃ |  |
Chemically-resistant septum is most commonly used. Its hardness is suitable for usage with an autosampler needle, it has high seal-ability and is suitable for multiple injections. It can be sued for many GC and GC-MS analyses. | ✓ |
| PTFE / Silicone / PTFE |  |
A septum with PTFE coating on both sides will have the highest chemical resistance. As breakage of the septum is unlikely to occur when a needle passes through, it is suitable for multiple injections, It is relatively expensive among septa. It is suitable for analyses requiring high accuracy, such as microanalysis. | ||
| Silicone / PI | 300℃ |  |
Elution of the bleeding components is low even if the temperature is kept at 300 #x2103;, enabling analysis at high temperatures, which had been difficult with a headspace sampler. | ✓ |
CQ (Certificated Quality) Vial Septum

The bleed of the septum from siloxane bonds is very low due to the use of high-quality silicon polymer and a specific cleaning technique. This confirms that there was an absence of elution components from the vial in random inspections using GC/MS and LC/MS. A mass spec quality certificate is included with each CQ vial kit.
Xtra Low Bleed HS Septum

Elution of the bleeding components is low even if the temperature is kept at 300 °C, enabling analysis at high temperatures, which had been difficult with a headspace sampler.
Cap

Screw Cap and Crimp Cap
Select the appropriate cap according to the vial. Since highly volatile solvents are often handled with GC/GC-MS, screw top or crimp top vials are generally used.
A crimp top vial requires a dedicated tool for attachment and detachment and takes time to open and close. At the same time, the risk of contamination is low, making it suitable for applications in the areas of food and forensic medicine where emphasis is placed on security.

Septum-free Cap
Contaminants from the septum can often hinder high-precision analysis and the effects are especially significant when performing injection operations multiple times.
- Septum-less cap
A cap that does not use a septum and can be used as a vial cap for 1.5 mL screw vials; however, the airtightness of these caps is inferior to caps that use a septum. - Xtra Clean Conical Cap
Xtra Clean Conical Caps are used with 4 mL vials into which cleaning solvents are put for the AOC series. Conical caps have a pre-hole opening so that septum-originated contaminants will not be generated.
For cleaning solvents, injection operations are performed repeatedly and the effects of contaminants from the septum are likely to occur. It is therefore recommended to use this cap.

Magnetic Cap
Cap made of steel that is used for multifunctional autosamplers. Compatible with vial conveyance using a magnet.


