Tomosynthesis, making the invisible visible
Shimadzu realized the world’s first practical use of Tomosynthesis on RF-table systems, SONIALVISION series, with the latest Flat Panel Detector and advanced Digital Imaging Technology.
This state-of-the-art imaging technology offers high quality multi-slice images to visualize the part which was invisible by the conventional plain radiography, in a simple and quick workflow, and at low exposure dose. Therefore, Tomosynthesis is now spotlighted more and more in the world.
What is “Tomosynthesis” ?
”Tomosynthesis” is a coined term from ‘Tomography’ and ‘Synthesis’.
It is a new type of imaging technology that fuses cone-beam CT reconstruction with digital image processing to produce images specified cross sections from a single tomography scan. It used the reconstruction method resulting from enhancement of Filtered Back Projection (FBP), and provides multiple slice images reconstructed from the volume data.

Standing position Tomosynthesis image of weight-loaded knee joints
What will be realized by Tomosynthesis ?
Reduce examination time and X-ray dose
Since the images of a specific cross section can be reconstructed from a single low dose tomography scan motion only, this technique requires less time and less x-ray dose to obtain multiple slice images than conventional linear tomography.
The short examination time would be very helpful to the stressed or immobile patients.
Free position tomography
Tomosynthesis by SONIALVISION allows recording of images at any angle required for diagnosis, including a variety of table angles or with the patient standing and reverse inclined position to apply gravity, which is not possible by CT scanners. It helps expand the examination range and remedy possibility.
Weight-loaded Tomosynthesis in standing position
High resolution images with less metal artifacts
The combination of high resolution FPD and our advanced imaging technology realizes excellent resolution Tomosynthesis images which are highly appreciated in the diagnoses of a micro-fracture etc.
Another key clinical benefit is that Tomosynthesis images has minimal influence from the metal artifacts that are usually seen on CT images. Therefore, Tomosynthesis is nowadays spotlighted in the orthopedics for the follow-up diagnoses to the patient with metal implants.
Precise Fracture Diagnosis
(Courtesy of Okitama Public General Hospital)
Clear visualization for callus formation
(Courtesy of Nara City Hospital)
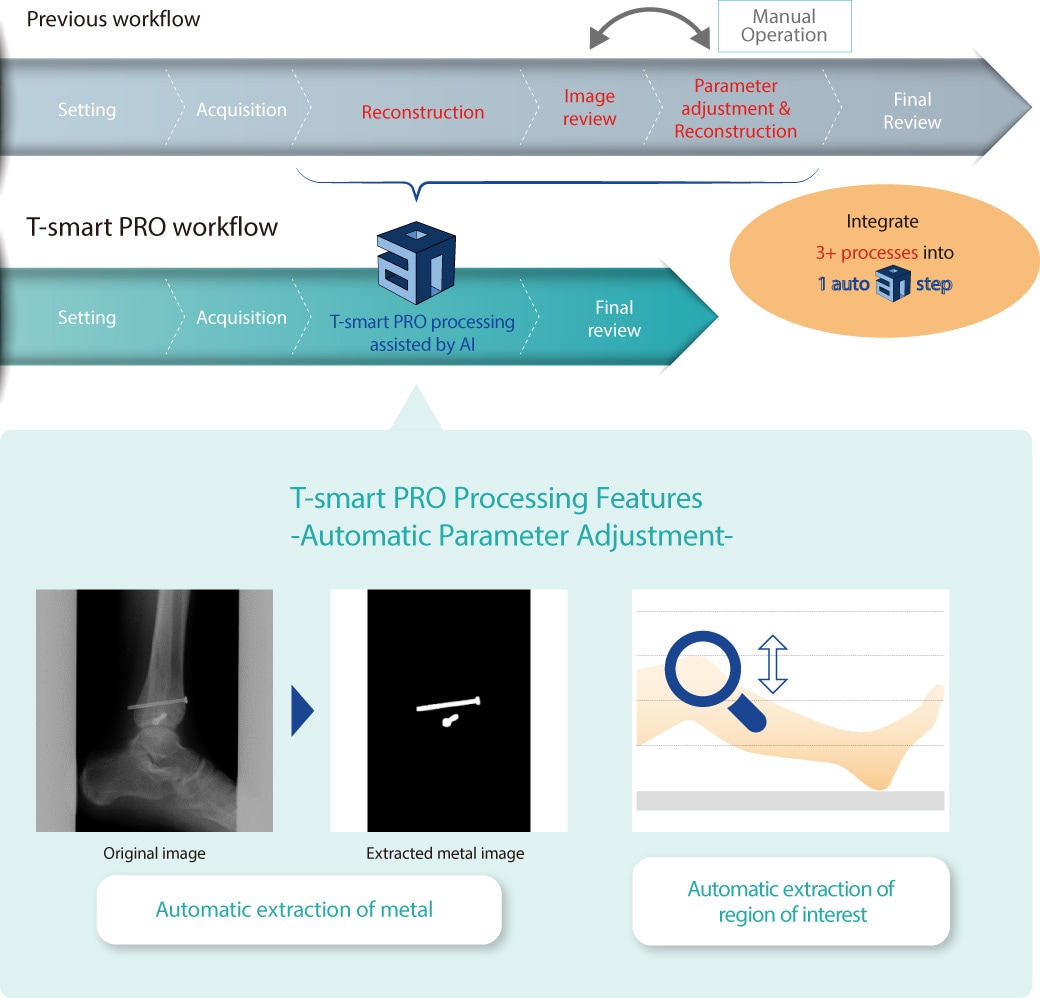
T-smart PRO assisted by AI Tomosynthesis-Shimadzu Metal Artifact Reduction Technology PRO
“T-smart PRO” is our latest and highest grade Tomosynthesis technology, providing tomographic images with less metal artifacts, in an efficient workflow utilizing deep learning technology.
Shimadzu metal artifact reduction technology with AI (Artificial Intelligence) image processing enables to focus on patient care by providing easy-to-interpret Tomosynthesis images with more efficient workflow.
Easy-to-interpret Tomosynthesis images minimizing metal artifacts
T-smart PRO provides enhanced Tomosynthesis images by further suppressing artifacts around metal objects using an iterative reconstruction method. This application greatly helps orthopedics especially for patients with metal implants or fixators, as it enables diagnoses the boundary between bone and implant very exactly.

Follow up of after BHA (Bipolar Hip Arthroplasty)
(Courtesy of Kanazawa University Hospital)
Efficient workflow assisted by Shimadzu AI technology
The entire workflow is so simple that anyone can obtain Tomosynthesis images with ease and efficient workflow. Shimadzu AI image processing technology automatically adjusts reconstruction parameters to simplify and optimize its workflows, so there is no need extensive skill and time.
* The AI (Artificial Intelligence) technology used in T-smart PRO is a "trained model" that was trained at some point and performed accuracy evaluation.
It doesn't continue learning after installation.
T-smart PRO clinical images
Follow up of after [left] BHA (Bipolar Hip Arthroplasty) and [right] TKA (Total Knee Arthroplasty)
The boundary between the artificial joint and bone is clearly depicted,
and it is useful for evaluation of implant-bone fixation.
Surgery repaired ulnar fracture
The fractures around fixing plate can be clearly observed by suppressing the metal artifacts.
Precise diagnosis of heel micro-fractures
Multiple slices of Tomosynthesis can show the micro-fracture in detail.
Compression fracture of the lumbar spine
Lumbar fractures that are difficult to visualize on radiographs because of overlap can be clearly observed.
Clear observation of pulmonary emphysema
A short scan time provides clear, blur-free lung images, and patients don't have to hold their breath for long periods.
This page may contain references to products that are not available in your country. Please contact us to check the availability of these products in your country.
Department of Medical Technology, Radiology Division, General Radiography Examination Room, Kurashiki Central Hospital
Simantocho Taisho Shinryosho
Department of Radiology, Kariya Toyota General Hospital
Chief Physician, Department of Radiology,
Guangdong Second Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangzhou, China
Vice Chairman, Imaging Expert Committee, China Medical Association
Department of Orthopaedics, Graduate School of Medical Science, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine1
Development of Multidisciplinary Promote for Physical Activity, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine2
Department of Radiology, Graduate School of Medical Science, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine3
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Japanese Red Cross Kyoto Daini Hospital4
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Nara City Hospital1,
Department of Radiology, Division of Medical Technology, Nara City Hospital2,
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Nara Medical University3
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Juntendo University
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Aizawa Hospital
Takumi Nakagawa1, and Hirotaka Kawano1
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Teikyo University1
Shimazaki Hospital2
Department of Radiology, Sendai Nishitaga Hospital
Yukihide Minoda1,Koichi Ichikawa1, and Hiroaki Nakamura1
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine1,
Ito Clinic, Osaka Shoulder Center2
Osaka International Cancer Institute, Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Section1
Osaka International Cancer Institute, Orthopedic Surgery (Musculoskeletal Oncology) and Rehabilitation Section2
Takeuchi Rheumatism Orthopedic Surgery Clinic
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tokyo Women's Medical University
Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Imamura General Hospital
Takanao Shimabukuro1, Yuichi Takano1, Hirohiko Inanami1,2
Iwai Orthopaedic Medical Hospital1, Inanami Spine and Joint Hospital2
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Kitasato University School of Medicine1, Kurokouchi Hospital2
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kainan Hospital1, Department of Arthroplastic Medicine, Nagoya City University2
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Saga University
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yufuin Hospital1 and Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Oita University2
Department of Radiology, Nippon Koukan Hospital
Department of Internal Medicine, Nippon Koukan Hospital
Department of Arthroplasty, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine,
Saga University
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tokyo Women's Medical University
Department of Central Radiology, Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital
Department of Radiology, Iida Hospital
Professor and Chairman
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tokyo Women's Medical University
Professor and Chair Dept. of Adult Reconstructive Surgery
Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, the 4th Clinical College of PKU
Department of Orthopedics, Mitsubishi Kyoto Hospital
Department of Radiological Technology, Mitsubishi Kyoto Hospital
Department of Endoscopy, Respiratory Endoscopy Division, National Cancer Center Hospital
Radiology Department, Shinshu University Hospital
Department of Gastroenterological Medicine,Tokyo Women's Medical University Hospital
Department of Radiology, Nara City Hospital
Spine Center, Seirei Hamamatsu General Hospital
Department of Radiology, Fussa Hospital
Diagnostic Imaging Center, Aizawa Hospital
Chiba Central Medical Center
Deputy Director, Director of Orthopedics, Director of Spine Center
Division of Clinical Radiology, Tottori University Hospital
Department of Radiology, Shingu Municipal Medical Center
Radiology Division, Dokkyo Medical University Koshigaya Hospital
-Targeting Lung Cancer Screening- (PDF 2.44MB)
Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center Hospital East
Division of Thoracic Oncology, National Cancer Center Hospital East
-Utility of Tomosynthesis in Orthopedic Surgery- (PDF 4.24MB)
Iwate Medical University Hospital,Central Department of Radiology
Medical Systems Division, Shimadzu Corporation
Medical Systems Division, Shimadzu Corporation,