
Society Challenges
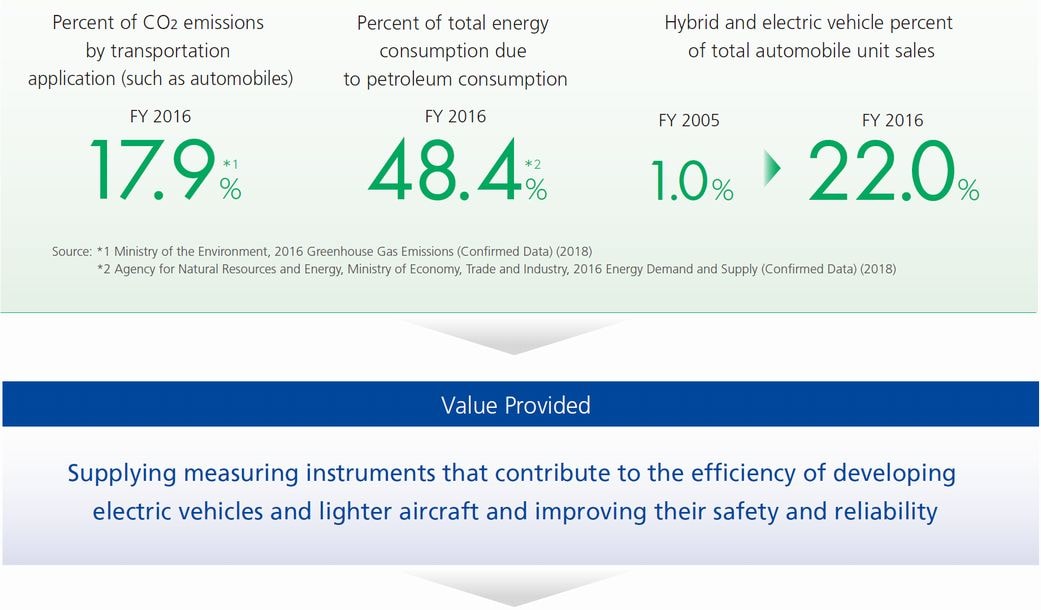
In recent years, global warming from increasing quantities of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions has increased the frequency of abnormal weather events throughout the world. Furthermore, the global increase in demand for energy has increased the use of petroleum, coal, natural gas, and other fossil fuels, which is causing problems with natural resource depletion. About 70 % of CO2 emissions in Japan are emitted from industry, with transportation-related applications (such as automobiles) accounting for 215 million tons of emissions, or 17.9 % of the total. Petroleum accounts for about 50 % of all energy consumption.
Contribution to SDGs
For transport equipment, such as automobiles and aircraft, there has been increasing technological development activity for developing new fuels to replace petroleum or to develop lighter structural materials that improve fuel efficiency. We will contribute to reducing our environmental impact by developing new measuring techniques and products or by reducing GHG emissions and resource mining, for example.

Feedback from a Partner
Joint Research with Shimadzu Supports Manufacturing Industries Around the World
The mission of the Dimensional Standards Group is to specify more sophisticated methods and official standards for measuring complex dimensions. As part of their activities, we have been involved in joint research with Shimadzu Corporation to achieve dimensional X-ray CT systems with guaranteed measurement accuracy. Results from the research are used to create the first dimensional X-ray CT system truly made in Japan, which is anticipated to meet the needs of advanced manufacturing industries not only in Japan, but also throughout the world.

Dr.Makoto Abe
Group Leader
Dimensional Standards Group
Research Institute of Engineering
Measurement
National Institute of Advanced
Industrial Science and Technology(AIST)
Measures by Shimadzu Corporation
Contributing to the Performance and Safety of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries, which function based on a chemical reaction between objects, are normally made by rolling a cathode, anode, and separator into a cylindrical shape. However, with the increasing popularity of electric vehicles, it is expected that lithium-ion batteries will require higher capacity and higher energy density levels. Consequently, a high-performance separator that is safer and able to withstand higher voltage levels are also being developed. To improve battery performance and other battery features, it is important to measure dimensions inside the battery to make sure the cathode, anode, or separator is not shifted out of position, for example. One technology used to accurately measure dimensions inside the batteries is X-ray computed tomography (CT), which enables three-dimensional measurements from cross sectional images of the interior. By using X-ray CT technology to maintain the performance and safety of lithium-ion batteries and thereby support the widespread adoption of lithium-ion batteries, we think about improving the global environment and contribute to creating a safe and secure society. Furthermore, given that Japan is a world leader in battery development, many companies and academic institutions in Japan are currently involved in researching and developing lithium-air batteries, which are a type of solid-state battery that has attracted attention as the next type of battery to follow lithium-ion batteries. Therefore, in addition to supporting such R&D activities with our measurement instruments, we released a dimensional X-ray CT system to support such measurements and respond to industry requirements for more precise measurement ability inside objects. Because the system can measure the actual status inside objects, it can be used to compare that status to design dimensions.

inspeXio SMX-225CT FPD HR
Microfocus X-Ray CT System

Cross Section Image of Model 18650
Lithium-Ion Rechargeable Battery
Contributing to Improving CFRP and CFRTP Performance and Reliability
Progress toward using lighter structural materials to improve fuel efficiency occurred earlier for aircraft than for other modes of transportation. Consequently, aluminum alloys and carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) materials have replaced steel as the main structural materials used for aircraft. Meanwhile, efforts to reduce the environmental impact of automobiles have also accelerated, due to the popularity of electric vehicles (EV) and plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHV). Furthermore, automotive manufacturers are now trying to reduce the weight of the main structures and exterior panels of automobiles, just as aircraft manufacturers did, while maintaining the strength and safety of automobiles. One of the new materials being used for that purpose is carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic (CFRTP). CFRTP is known to offer superior moldability and workability than the CFRP materials used for aircraft structures. Given the current boom in researching and developing CFRTP materials for use in automobiles, analysis and measurement technologies for evaluating new materials are essential for such R&D work. Analytical and measuring instruments are used for a diverse range of CFRTP evaluation applications, such as for determining the composition, molecular weight, chemical structure, or thermal properties of polymers, or for evaluating the mechanical properties of composite materials or for non-destructive inspection inside molding models. The range of such applications is also expected to expand to a whole new level in the future.

AUTOGRAPH AG-X plus Universal Testing Machine

HITS-X High-Speed Impact Testing Machine


